The Syria Deception: Understanding the geopolitical and psychological war against Syria
By Swiss Propaganda Research
March 05, 2020 "Information Clearing House" - What is the Syria war about?
Nor is the Syria war a religious war, for Syria was and still is one of the most secular countries in the region, and the Syrian army – like its direct opponents – is itself mainly composed of Sunnis.
But the Syria war is also not a pipeline war, as some critics suspected, because the allegedly competing gas pipeline projects never existed to begin with, as even the Syrian president confirmed.
Instead, the Syria war is a war of conquest and regime change, which developed into a geopolitical proxy war between NATO states on one side – especially the US, Great Britain and France – and Russia, Iran, and China on the other side.
In fact, already since the 1940s the US has repeatedly attempted to install a pro-Western government in Syria, such as in 1949, 1956, 1957, after 1980 and after 2003, but without success so far. This makes Syria – since the fall of Libya – the last Mediterranean country independent of NATO.
Thus, in the course of the „Arab Spring“ of 2011, NATO and its allies, especially Israel and the Gulf States, decided to try again. To this end, politically and economically motivated protests in Syria were used and were quickly escalated into an armed conflict.

NATO’s original strategy of 2011 was based on the Afghanistan war of the 1980s and aimed at conquering Syria mainly through positively portrayed Islamist militias (so-called „rebels“). This did not succeed, however, because the militias lacked an air force and anti-aircraft missiles.
Hence from 2013 onwards, various poison gas attacks were staged in order to be able to deploy the NATO air force as part of a „humanitarian intervention“ similar to the earlier wars against Libya and Yugoslavia. But this did not succeed either, mainly because Russia and China blocked a UN mandate.
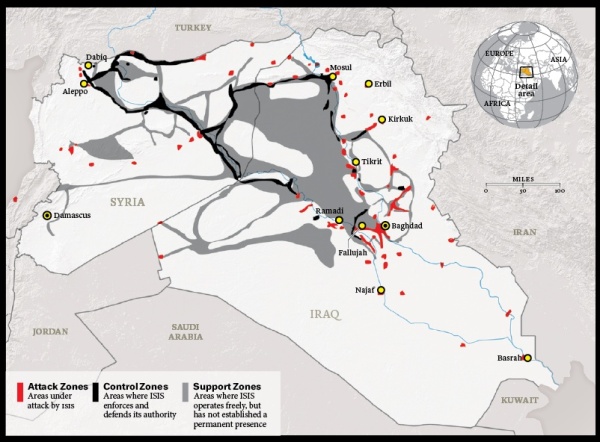
As of 2014, therefore, additional but negatively portrayed Islamist militias („terrorists“) were covertly established in Syria and Iraq via NATO partners Turkey and Jordan, secretly supplied with weapons and vehicles and indirectly financed by oil exports via the Turkish Ceyhan terminal.
Media-effective atrocity propaganda and mysterious „terrorist attacks“ in Europe and the US then offered the opportunity to intervene in Syria using the NATO air force even without a UN mandate – ostensibly to fight the „terrorists“, but in reality still to conquer Syria and topple its government.
By the end of 2016, the Syrian army thus succeeded in recapturing the city of Aleppo.
From 2016 onwards, NATO therefore switched back to positively portrayed but now Kurdish-led militias (the SDF) in order to still have unassailable ground forces available and to conquer the Syrian territory held by the previously established „terrorists“ before Syria and Russia could do so themselves.
This led to a kind of „race“ to conquer cities such as Raqqa and Deir ez-Zor in 2017 and to a temporary division of Syria along the Euphrates river into a (largely) Syrian-controlled West and a Kurdish (or rather American) controlled East (see map above).
This move, however, brought NATO into conflict with its key member Turkey, because Turkey did not accept a Kurdish-controlled territory on its southern border. As a result, the NATO alliance became increasingly divided from 2018 onwards.
Turkey now fought the Kurds in northern Syria and at the same time supported the remaining Islamists in the north-western province of Idlib against the Syrian army, while the Americans eventually withdrew to the eastern Syrian oil fields in order to retain a political bargaining chip.
While Turkey supported Islamists in northern Syria, Israel more or less covertly supplied Islamists in southern Syria and at the same time fought Iranian and Lebanese (Hezbollah) units with air strikes, but ultimately without success: the militias in southern Syria had to surrender in 2018.
Ultimately, some NATO members tried to use a confrontation between the Turkish and Syrian armies in the province of Idlib as a last option to escalate the war. In addition to the situation in Idlib, the issues of the occupied territories in the north and east of Syria remain to be resolved, too.
Russia, for its part, has tried to draw Turkey out of the NATO alliance and onto its own side as far as possible. Modern Turkey, however, is pursuing a rather far-reaching geopolitical strategy of its own, which is also increasingly clashing with Russian interests in the Middle East and Central Asia.
As part of this geopolitical strategy, Turkey in 2015 and 2020 even used the so-called »weapon of mass migration«, which may serve to destabilize both Syria (so-called strategic depopulation) and Europe, as well as to extort financial, political or military support from the European Union.
What role did the Western media play in this war?
The task of NATO-compliant media was to portray the war against Syria as a „civil war“, the Islamist „rebels“ positively, the Islamist „terrorists“ and the Syrian government negatively, the alleged „poison gas attacks“ credibly and the NATO intervention consequently as legitimate.
An important tool for this media strategy were the numerous Western-sponsored „media centres“, „activist groups“, „Twitter girls“, „human rights observatories“ and the like, which provided Western news agencies and media with the desired images and information.
Since 2019, NATO-compliant media moreover had to conceal or discredit various leaks and whistleblowers that began to prove the covert Western arms deliveries to the Islamist „rebels“ and „terrorists“ as well as the staged „poison gas attacks“.
But if even the „terrorists“ in Syria were demonstrably established and equipped by NATO states, what role then did the mysterious „caliph of terror“ Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi play? He possibly played a similar role as his direct predecessor, Omar al-Baghdadi – who was a phantom.
Thanks to new communication technologies and on-site sources, the Syria war was also the first war about which independent media could report almost in real-time and thus for the first time significantly influenced the public perception of events – a potentially historic change.
No comments:
Post a Comment